Last_Error: Error 'Duplicate entry '9999707' for key 'PRIMARY'' on query. Default database: 'teguht'. Query: 'INSERT INTO sessions (session_id, data_key, data_value, serialized) VALUES ('E6iNeYTAMo4FBl2gpoicy0kWVqYfTygv','LastScreenOverview','Action=AgentFAQExplorer;SortBy=FAQID;CategoryID=0;Nav=;OrderBy=Down;StartHit=1','0'),('E6iNeYTAMo4FBl2gpoicy0kWVqYfTygv','LastScreenView','Action=AgentFAQExplorer;SortBy=FAQID;CategoryID=0;Nav=;OrderBy=Down;StartHit=1','0'),('E6iNeYTAMo4FBl2gpoicy0kWVqYfTygv','LastViewedCategory','0','0'),('E6iNeYTAMo4FBl2gpoicy0kWVqYfTygv','UserFAQOverviewAgentFAQExplorer','Small','0'),('E6iNeYTAMo4FBl2gpoicy0kWVqYfTygv','UserLastRequest','1537333985','0')
Wednesday, September 19, 2018
.::: How to Simple Troubleshooting Error 'Duplicate entry '9999707' on slave/master MySQL/MariaDB include repair table database:::.
1. Get Error on replication/mirroring MySQL/MariaDB
Last_Error: Error 'Duplicate entry '9999707' for key 'PRIMARY'' on query. Default database: 'teguht'. Query: 'INSERT INTO sessions (session_id, data_key, data_value, serialized) VALUES ('E6iNeYTAMo4FBl2gpoicy0kWVqYfTygv','LastScreenOverview','Action=AgentFAQExplorer;SortBy=FAQID;CategoryID=0;Nav=;OrderBy=Down;StartHit=1','0'),('E6iNeYTAMo4FBl2gpoicy0kWVqYfTygv','LastScreenView','Action=AgentFAQExplorer;SortBy=FAQID;CategoryID=0;Nav=;OrderBy=Down;StartHit=1','0'),('E6iNeYTAMo4FBl2gpoicy0kWVqYfTygv','LastViewedCategory','0','0'),('E6iNeYTAMo4FBl2gpoicy0kWVqYfTygv','UserFAQOverviewAgentFAQExplorer','Small','0'),('E6iNeYTAMo4FBl2gpoicy0kWVqYfTygv','UserLastRequest','1537333985','0')
Last_Error: Error 'Duplicate entry '9999707' for key 'PRIMARY'' on query. Default database: 'teguht'. Query: 'INSERT INTO sessions (session_id, data_key, data_value, serialized) VALUES ('E6iNeYTAMo4FBl2gpoicy0kWVqYfTygv','LastScreenOverview','Action=AgentFAQExplorer;SortBy=FAQID;CategoryID=0;Nav=;OrderBy=Down;StartHit=1','0'),('E6iNeYTAMo4FBl2gpoicy0kWVqYfTygv','LastScreenView','Action=AgentFAQExplorer;SortBy=FAQID;CategoryID=0;Nav=;OrderBy=Down;StartHit=1','0'),('E6iNeYTAMo4FBl2gpoicy0kWVqYfTygv','LastViewedCategory','0','0'),('E6iNeYTAMo4FBl2gpoicy0kWVqYfTygv','UserFAQOverviewAgentFAQExplorer','Small','0'),('E6iNeYTAMo4FBl2gpoicy0kWVqYfTygv','UserLastRequest','1537333985','0')
Thursday, August 30, 2018
.::: How to Install Openstack Stein, Rocky, Quenns, Pike Using Bash Script one Push :::.
OpenStack is developed and released around 6-month cycles. After the initial release, additional stable point releases will be released in each release series. You can find the detail of the various release series here on their series page
1. Check new version openstack on this lab. openstack rocky <lastest version>
### yum install -y centos-release-openstack-rocky
### yum install -y centos-release-openstack-queens
### yum install -y centos-release-openstack-pike
Tuesday, August 28, 2018
.::: How To Redundant Set Master to Master(Replica) and Master to Slave(Mirroring) On MySQL (Include MariaDB) :::.
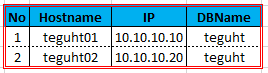
A. Configuring MySQL Server on Server01
1. Edit & add db file conf /etc/my.cnf
server_id=1
replicate-do-db=teguht
#bind-address=10.10.10.10
log-bin = mysql-bin
binlog_do_db = teguht
set global read_only=on;
set global read_only=off;
skip-slave-start
set global read_only=1;
======
[root@MariaDB002 ~]# cat /etc/my.cnf.d/server.cnf
## -> only 1 database (teguhth)
[mariadb]
server_id=1
replicate-do-db=teguhth
#bind-address=10.10.10.10
log-bin = mysql-bin
binlog_do_db = teguhth
## -> more 2 database (teguhth, secretdb, labdb)
[mariadb]
server_id=1
replicate-do-db=teguhth
replicate-do-db=secretdb
replicate-do-db=labdb
#bind-address=10.10.10.10
log-bin = mysql-bin
binlog_do_db = teguhth
binlog_do_db = secretdb
binlog_do_db = labdb
sample log
.::: How to Install and Configuration PCS, COROSYNC, and Pacemaker for HA(High Availability) On Linux, Centos, Rhel :::.
Corosync is an open source cluster engine used to implement high availability within applications. Commonly referred to as a messaging layer, Corosync provides a cluster membership and closed communication model for creating replicated state machines, on top of which cluster resource managers like Pacemaker can run. Corosync can be seen as the underlying system that connects the cluster nodes together, while Pacemaker monitors the cluster and takes action in the event of a failure.
This tutorial will demonstrate how to use Corosync and Pacemaker to create a high availability (HA) infrastructure on DigitalOcean with CentOS 7 servers and Floating IPs. To facilitate the process of setting up and managing the cluster nodes, we are going to use PCS, a command line interface that interacts with both Corosync and Pacemaker.A. Pre Activity
This tutorial will demonstrate how to use Corosync and Pacemaker to create a high availability (HA) infrastructure on DigitalOcean with CentOS 7 servers and Floating IPs. To facilitate the process of setting up and managing the cluster nodes, we are going to use PCS, a command line interface that interacts with both Corosync and Pacemaker.A. Pre Activity
Thursday, May 17, 2018
.::: Log Output Create Tenant Project, User, Keypair, Network, Floating, upload Image, Flavors, Instance In Openstack Using CLI :::.
this post as example log output from cli to Create Tenant Project, User, Keypair, Network, Floating, upload Image, Flavors, Instance
1. Create Project & User
# source keystonerc_admin
# openstack project create --description teguht-project-des teguht-project
# openstack user create --project teguht-project --password teguht --email teguh.triharto@microsoft.com teguht
# openstack project list
# openstack project show teguht-project
# openstack user list
# openstack user show teguht
# openstack user role list
1. Create Project & User
# source keystonerc_admin
# openstack project create --description teguht-project-des teguht-project
# openstack user create --project teguht-project --password teguht --email teguh.triharto@microsoft.com teguht
# openstack project list
# openstack project show teguht-project
# openstack user list
# openstack user show teguht
# openstack user role list
.::: Create Tenant (Project, User, Keypair, Network, Floating, upload Image, Flavors) & launch Instance In Openstack Using CLI :::.
1. Create Project & User
# source keystonerc_admin
# openstack project create --description teguht-project-des teguht-project
# openstack user create --project teguht-project --password teguht --email teguh.triharto@microsoft.com teguht
# openstack project list
# openstack project show teguht-project
Friday, April 20, 2018
.::: Setting NFS Server & NFS Client (FreeNAS) on Centos7 to Connect Network Share :::.
Network File System (NFS) is a distributed file system protocol originally developed by Sun Microsystems in 1984, allowing a user on a client computer to access files over a computer network much like local storage is accessed. NFS, like many other protocols, builds on the Open Network Computing Remote Procedure Call (ONC RPC) system. The NFS is an open standard defined in Request for Comments (RFC), allowing anyone to implement the protocol.
A. Server (example 10.10.10.10 & /home/mounting)
1. Install Package
# yum install nfs* rcpbind
A. Server (example 10.10.10.10 & /home/mounting)
1. Install Package
# yum install nfs* rcpbind
Tuesday, April 10, 2018
.::: Install OpenStack Newton All In One with Heat Service on CentOS 7 (Lab Verified) :::.
 OpenStack is a free and open-source software platform for cloud computing, mostly deployed as infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), whereby virtual servers and other resources are made available to customers.The software platform consists of interrelated components that control diverse, multi-vendor hardware pools of processing, storage, and networking resources throughout a data center. Users either manage it through a web-based dashboard, through command-line tools, or through RESTful web services.
OpenStack is a free and open-source software platform for cloud computing, mostly deployed as infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), whereby virtual servers and other resources are made available to customers.The software platform consists of interrelated components that control diverse, multi-vendor hardware pools of processing, storage, and networking resources throughout a data center. Users either manage it through a web-based dashboard, through command-line tools, or through RESTful web services.1. Disable SELinux
[root@openstack /]# cat /etc/selinux/config
Friday, March 16, 2018
.::: Create CDEF's on Cacti to Multiple or Division or other Calculation Mathematical Functions :::.
CDEFs allow you to apply mathematical functions to graph data to alter output. The concept of a CDEF comes straight from RRDTool, and are written in reverse polish notation (RPN). For more information regarding the syntax of CDEFs,
1. Console -> Management -> CDEF's -> New
Name : Reamur
2. fill CDEF Item
cdef=CURRENT_DATA_SOURCE,4,*,5,/
1. Console -> Management -> CDEF's -> New
Name : Reamur
2. fill CDEF Item
cdef=CURRENT_DATA_SOURCE,4,*,5,/
Tuesday, March 13, 2018
.::: Create Graph Template Cacti base on OID/MIB :::.
Once one or more data sources are defined, an RRDTool graph can be created using the data. Cacti allows you to create almost any imaginable RRDTool graph using all of the standard RRDTool graph types and consolidation functions. A color selection area and automatic text padding function also aid in the creation of graphs to make the process easier.
Not only can you create RRDTool based graphs in cacti, but there are many ways to display them. Along with a standard "list view" and a "preview mode", which resembles the RRDTool frontend 14all, there is a "tree view", which allows you to put graphs onto a hierarchical tree for organizational purposes.
base on sample http://teguhth.blogspot.co.id/2018/01/monitoring-oidmib-temperature-fan-speed.html
A. Create Data Template
1. Console -> Data Template -> Add
2. Fill Data Template
Data Templates
Name : Temperature @ Ocelot
Not only can you create RRDTool based graphs in cacti, but there are many ways to display them. Along with a standard "list view" and a "preview mode", which resembles the RRDTool frontend 14all, there is a "tree view", which allows you to put graphs onto a hierarchical tree for organizational purposes.
base on sample http://teguhth.blogspot.co.id/2018/01/monitoring-oidmib-temperature-fan-speed.html
A. Create Data Template
1. Console -> Data Template -> Add
2. Fill Data Template
Data Templates
Name : Temperature @ Ocelot
Wednesday, February 7, 2018
.::: How to configure remote logging with rsyslog(Enable syslog) On Linux/Rhel/Centos :::.
In RHEL-6 rsyslog is default logging daemon, In RHEL-5 rsyslog is available but not installed by default.
1. Install rsyslog
# yum -y install rsyslog
2. Configure the remote server(CLIENT) to accept remote log messages using TCP/UDP.
Uncomment the following lines in the MODULES section of /etc/rsyslog.conf
[root@TeguhClientSyslog ~]# cat /etc/rsyslog.conf
.....
# Provides UDP syslog reception
#$ModLoad imudp
#$UDPServerRun 514
1. Install rsyslog
# yum -y install rsyslog
2. Configure the remote server(CLIENT) to accept remote log messages using TCP/UDP.
Uncomment the following lines in the MODULES section of /etc/rsyslog.conf
[root@TeguhClientSyslog ~]# cat /etc/rsyslog.conf
.....
# Provides UDP syslog reception
#$ModLoad imudp
#$UDPServerRun 514
Tuesday, February 6, 2018
.::: OID Memory Utilization for Monitoring Windows, Linux :::.
This resource displays linear or radial gauges of both the percentage load on the CPU of the selected node and the percentage of available MEMORY on the selected node over the current monitoring period. Reported values are updated regularly, on the Polling Interval.
1. OID for Memory Utilization
hrSWRunIndex hrSWRunIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.25.4.2.1.1 Memory Index
hrSWRunName hrSWRunName 1.3.6.1.2.1.25.4.2.1.2 Memory Name
hrSWRunPerfMem hrSWRunPerfMem 1.3.6.1.2.1.25.5.1.1.2 Memory Usage
hrMemorySize hrMemorySize 1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.2 mem total Memory Total
[root@TeguhLab ~]# snmpwalk -v2c -c public 10.10.10.10 sysDescr
SNMPv2-MIB::sysDescr.0 = STRING: Hardware: Intel64 Family 6 Model 62 Stepping 4 AT/AT COMPATIBLE - Software: Windows Version 6.0 (Build 6002 Multiprocessor Free)
[root@TeguhLab ~]#
Thursday, February 1, 2018
.::: OID CPU Utilization for Monitoring CPU Windows, Linux, Appliance & Other :::.
CPU utilization is the sum of work handled
by a Central Processing Unit. It is also used to estimate system
performance. CPU utilization can vary according to the type and amount
of computing task because some tasks require heavy CPU time while others
require less CPU time. Process time is another name for CPU time and is
the amount of time used by a CPU for processing instruction of an
operating system or a computer program. CPU time is quantified in clock
ticks or seconds. CPU utilization
shows the burden on a processor in terms of percentage that indicates
if any changes are to be made in the system otherwise it may get
exhausted of capacity.
CPU utilization can be calculated by using the following formulas.
Let us define CPU utilization as U
U = 100% - (Percentage of time that is spent in idle task)
% time in idle task =
(Take the average time period of background task without load) * 100%
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(Avg. period of background task including some load)
CPU utilization can be calculated by using the following formulas.
Let us define CPU utilization as U
U = 100% - (Percentage of time that is spent in idle task)
% time in idle task =
(Take the average time period of background task without load) * 100%
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(Avg. period of background task including some load)
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Popular Posts
-
Sertifikasi profesional, kadang hanya disebut dengan sertifikasi atau kualifikasi saja, adalah suatu penetapan yang diberikan oleh ...
-
SQL atau Structured Query Language) adalah sebuah bahasa yang digunakan untuk mengakses data dalam basis data relasional. Bahasa ini sec...
-
bagaimana cara mengubah hostid di Solaris The Hostid is a globally unique ID for a Sun Solaris Machine. Sometimes, you need to change t...
-
DNSPerf and ResPerf are free tools developed by Nominum that make it simple to gather accurate latency and throughput metrics for Domain ...
-
1. Check Host ID Solaris The Hostid is a globally unique ID for a Sun Solaris Machine. Sometimes, you need to change this hostid for ...

















